E-Government Development in South Africa
According to the 2022 UN Survey on E-Government Development, South Africa has become the continent’s leader in e-Government development with an EGDI (E-Government Development Index) value of 0.7. Digital development in South Africa is guided by the National Development Plan: Vision 2030 developed in 2012 by the National Planning Commision with the objective of making South Africa an inclusive digital society. The National e-Government Strategy and Roadmap, worked out in 2017 by the Telecommunications and Postal Services Department (The Department of Communications and Digital Technologies since 2019), outlines a new approach to electronic government development and sets a programme of action. As stated in the Strategy, more focused attention was planned to be given to infrastructure development, acceleration of the expansion of e-Government services and development of e-Government platforms.
State Information Technology Agency (SITA), overseen by the Department of Communications and Digital Technologies, is the industry leader and is in charge of execution of the Strategy and Roadmap. As stated in the SITA 2020-2024 Strategic Plan, the Agency has been a driving force behind the digitisation of the public sector.
Public Services
SITA has implemented the e-Government Portal that serves as a single point of entry to more than 100 services, including birth, health, education, employment and social services. The platform provides G2B and G2C services. All public services are interoperable and can be accessed through the website of the Government of South Africa.

Source: South African e-Service Portal (main page)
Identification and Biometrics
National Population Register (NPR) operated by the Department of Home Affairs (DHA) is used to verify the identity, status and rights of citizens. The NPR contains biometrics (thumbprints and facial biometric data). However, under the broad ICT Modernisation Programme, initiated by the DHA in 2012 and aimed at refurnishing the department’s delivery systems, the National Identity System (NIS) will replace the NPR. According to the Official Identity Management Policy published in 2020, the new system will facilitate the security and reliability of civil and immigration status bound to identity and biometric data. The NIS is expected to be put into operation by March 2024.
The Department of Home Affairs allows citizens to submit ID and passport applications online as well as make online payments for applications via eHomeAffairs. The Smart ID Card, which replaces the green ID book (a previous type of identification document), has a unique identity number and stores the biometrics of a person. In order to register on the website an ID Number is required.
The ABIS (Automated Biometric Identification System) project started in 2016 and conducted by the Department of Home Affairs is an upcoming integrated multi-modal system. ABIS is expected to serve as a centralised source for biometric authentication across public and private institutions. Fingerprints and facial recognition currently stored within the Home Affairs National Identification System (HANIS) will be transferred to the new system.
The use of electronic signatures in South Africa is regulated by the Electronic Communications and Transactions Act 25 (ECTA) of 2002. The act distinguishes an electronic signature and an advanced electronic signature. The latter requires a digital certificate issued by an accredited service provider, viz. the one that has been designated as a preferred authentication service provider with its products accredited by the South African Accreditation Authority. According to the Electronic Signature Guidelines, South Africa Post Office (SAPO) and Lawtrust are the accredited authentication service provides under the ECT Act. SAPO is the provider preferred by the Government.
Source: eHomeAffairs (main page)
Payment Systems
The South African Multiple Option Settlement (SAMOS) system is a real-time gross settlement system (RTGS) operated by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) which provides domestic settlement services. Regional settlement services are processed by the South African Development Community (SADC)-RTGS system that was put into operation in 2013.
In 2018, the SARB introduced the National Payment System Framework and Strategy: Vision 2025 with the aim of raising awareness on electronic payments.
G2B Services
BizPortal is a platform developed by the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission (CIPC) with the objective of alleviating business operations in South Africa and eliminating the paper-based approach. The Portal offers company registration and a variety of related services including tax registration and domain name registration.
SME South Africa platform grants access to a vast array of business guides and reviews of business software and technical tools. Within this platform citizens can also find funding for their businesses. After filling in the form on the website the person is connected with the lenders. The partners of SME South Africa are Lulalend, a privately held company financed by the Venture Capital, Retail Capital, a division of TymeBank Limited, and Genfin, which is a part of the Genfin Holdings Group, an investment company operating in South Africa and the UK.
Source: BizPortal (services page)
Healthcare
The Health Patient Registration System managed by the Department of Health provides the Patient Registry and the Master Patient Index utilising citizen’s unique identification number. The Home Affairs National Identification System (HANIS) can be used for the identification of patients as well. The System enables medical workers to access the demographic information and medical records of the patients.
The National Health Insurance (NHI) is a health financing system designed to provide access to health services free of charge for all the citizens. Citizens can take advantage of the health facilities using an NHI Card.
The Department of Health grants the ability to improve one’s professional skills by enrolling on a course within the Knowledge Hub. The platform offers a vast variety of courses and webinars in the medical sphere as well as allows to use eLibrary.
Source: KnowledgeHub (courses page)
Public Procurement
The eTender Publications Portal managed by the Office of the Chief Procurement Officer (OCPO) is a website where all public sector tender opportunities are published. Information on Procurement Data and Procurement Plans is also provided.
The service was introduced in order to reduce government expenditure on public procurement procedures since, according to the OECD calculations based on the data from Government Finance Statistics, South Africa ranked 2nd on the continent (after Rwanda) in terms of government procurement spending as percentage of GDP. As per IMF ‘Public Procurement In South Africa: Issues And Reform Options’ report (2023), in 2021/2022 fiscal year the public procurement spending in South Africa comprised 15% of GDP.
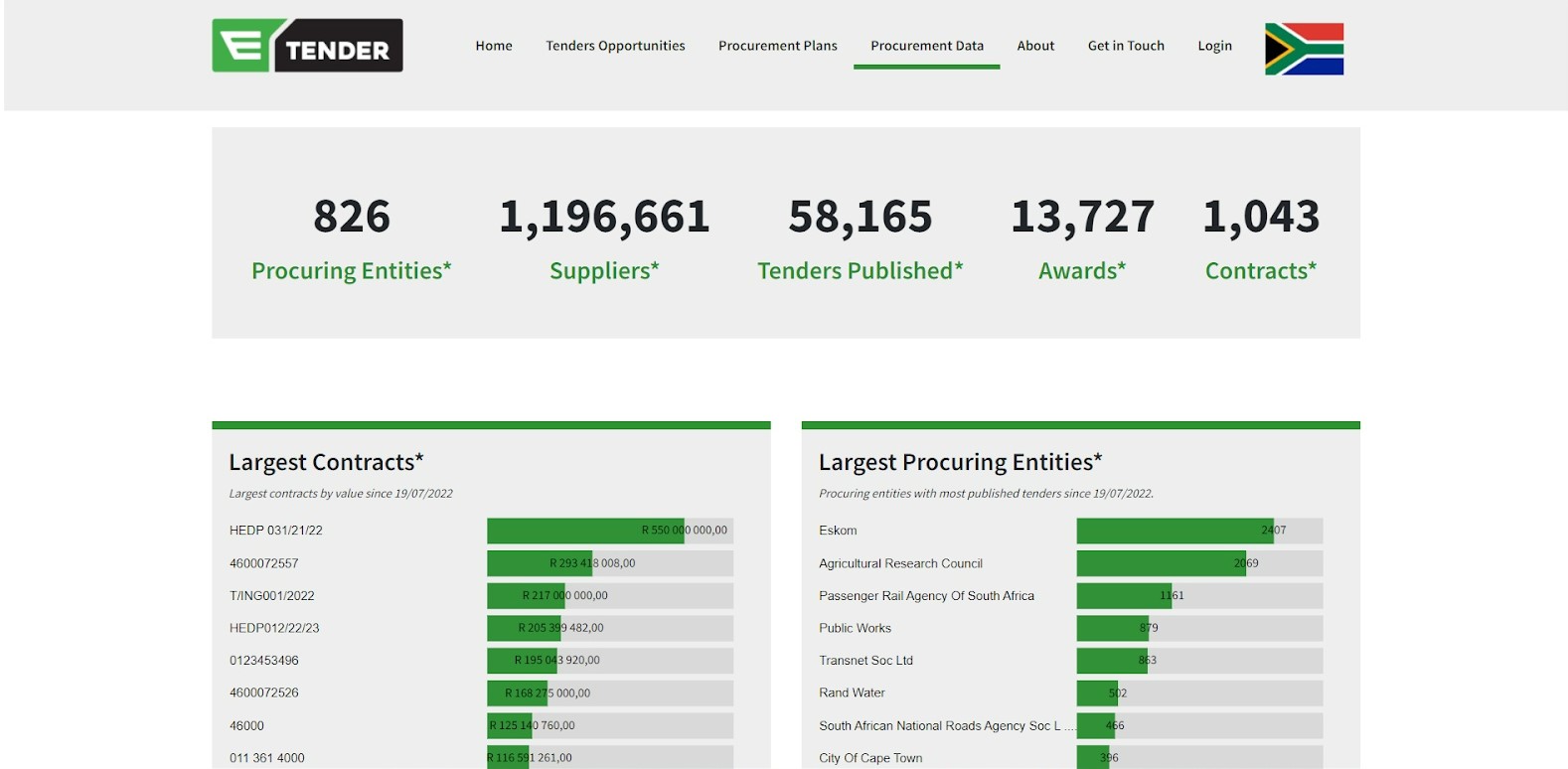
Source: eTender (main page)
Legislation
The documents and legal acts of South Africa can be accessed through the website of the Government. Keyword search and filters on document type and subject are available.
Labour
Employment Services of South Africa (ESSA) allows both individuals and organisations to search a database operated by the Department of Labour. Individuals have an opportunity to browse employment possibilities, while organisations may post the information on the open positions in the company.
Employment Equity Online Reporting (EE) is an online service for employers to submit their employment equity reports in compliance with the Employment Equity Act, which was adopted with the purpose of promoting equal opportunities and fair treatment in employment. The information on the login procedure and deadlines for the submission are provided on the home page of the portal.
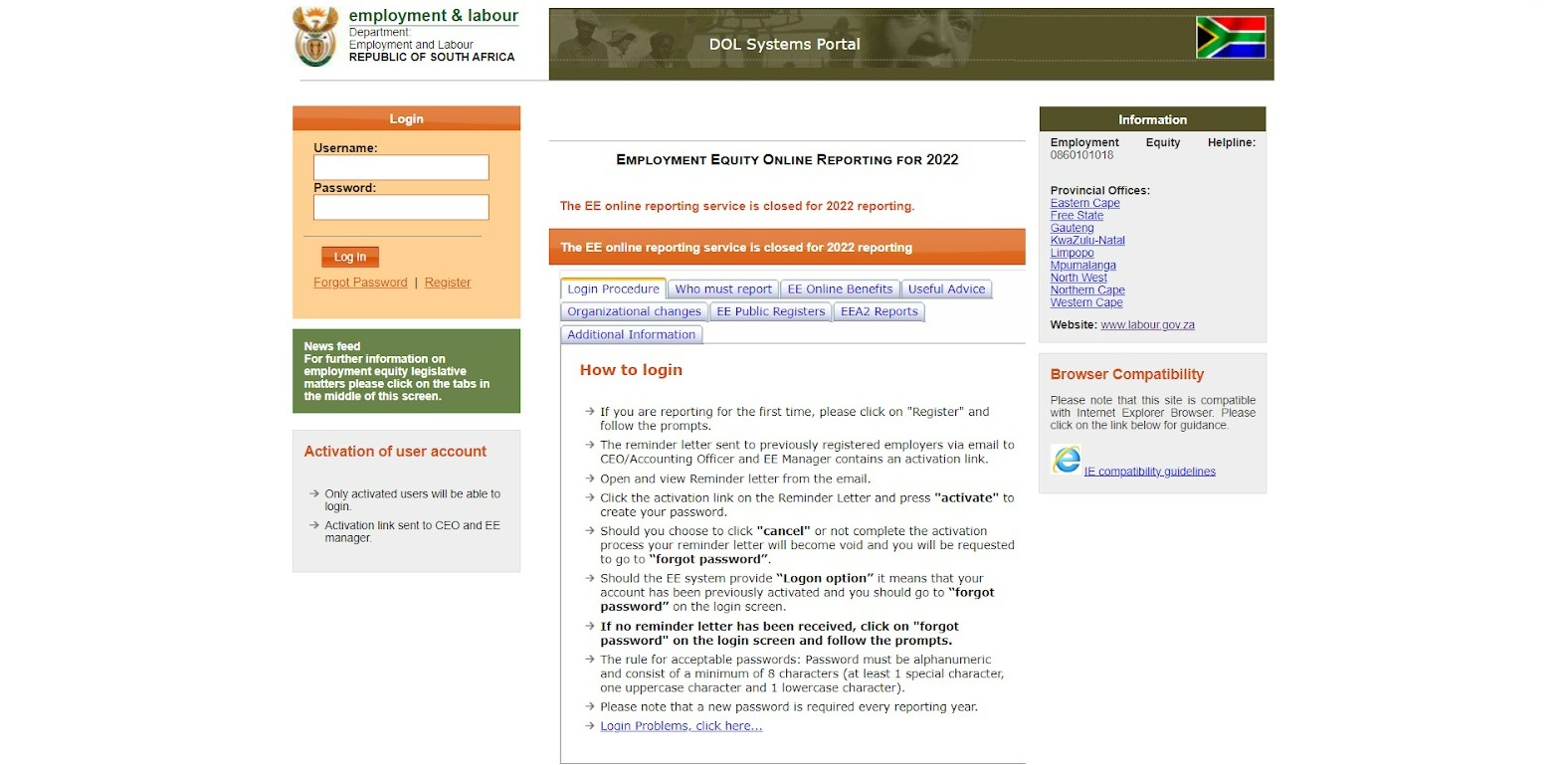
Source: Employment Equity Online Reporting (EE) (main page)
Tourism
The Government of South Africa enables tourists to access the South African Tourism website. The website consists of 4 sections, namely, Corporate and media, Travel, Travel Trade and Business events. For instance, the ‘travel’ section stores information on tourist activities, destinations and events, while the ‘business events’ part enables to discover the meeting venues.
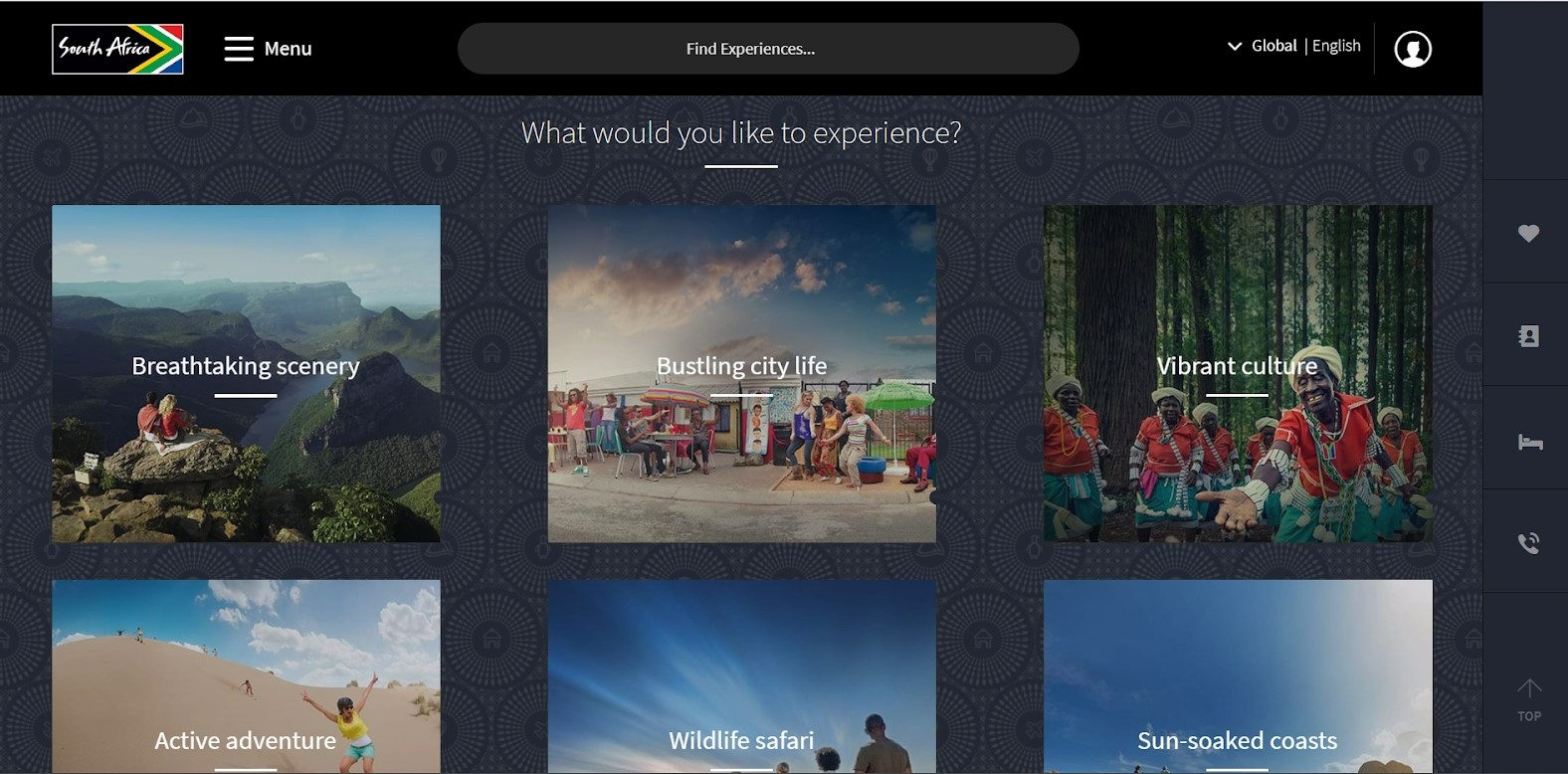
Source: South African Tourism (‘travel’ page)
e-Taxes
South African Revenue Service (SARS) eFiling platform serves as a tool for submitting tax returns and declarations and provides a range of related services, including registration for income tax, tax product registration, and filling income tax returns. Taxpayers, tax specialists, enterprises and organisations are able to register, submit declarations and make payments within the platform.
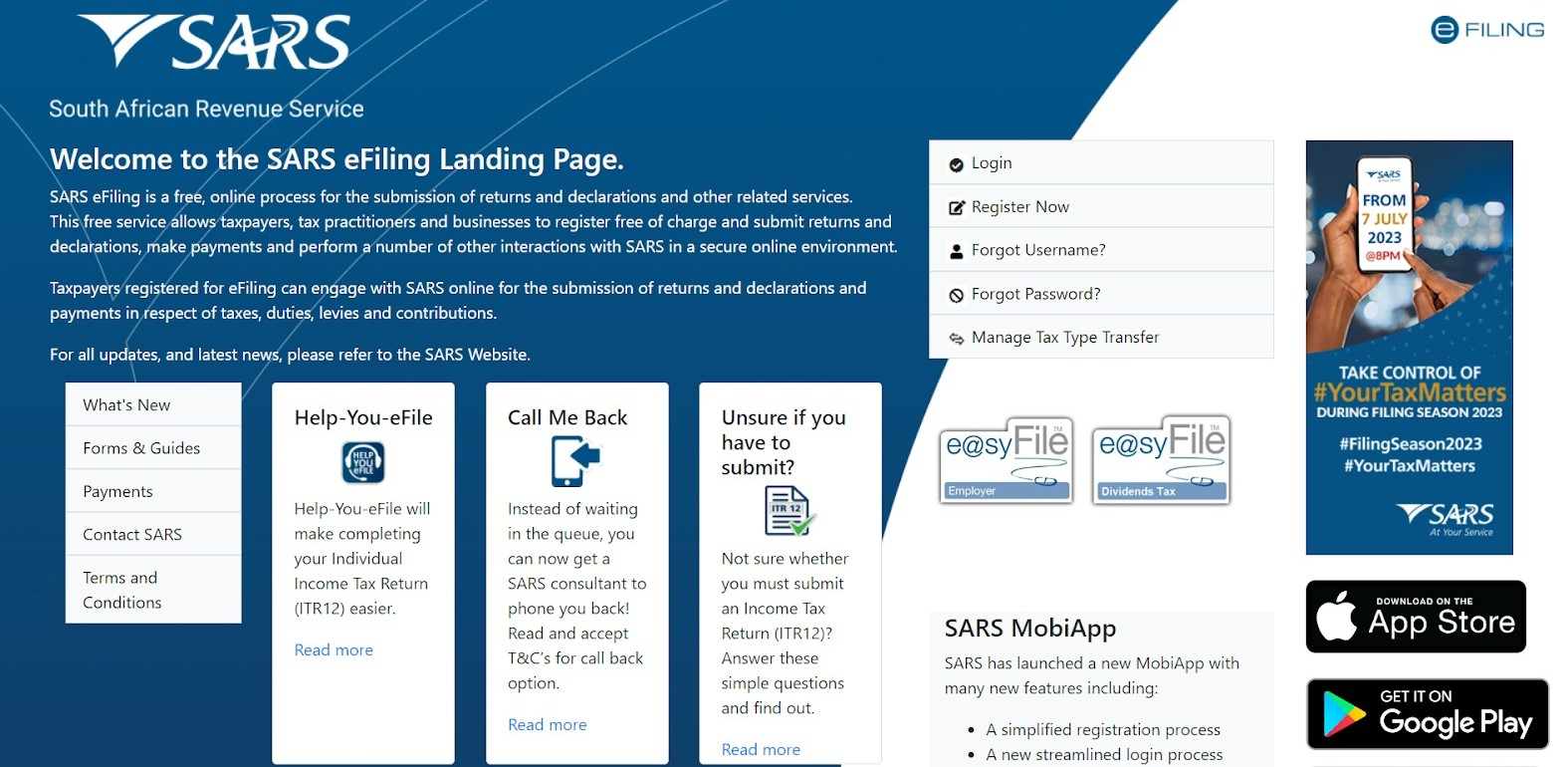
Source: SARS eFiling (main page)
Budget Data
Vulekamali is a website which stores South Africa online budget data. Users can download a pdf file of a national budget review, explore interactive Consolidated Budget Summary and National Budget Summary and examine the budget of each department.

Source: Vulekamali (main page)
Cloud Computing
The establishment of the Government Private Cloud is a project of SITA. The work on the project began in 2014. The Government Private Cloud Ecosystem (GPCE), built in partnership with Huawei, IBM and Gijima, was launched in 2018. The objective of the Agency was to build and operate a private cloud in order to facilitate interoperability of all South African Government departments. The project comprised providing an open data platform and developing policy framework to direct implementation of Cloud computing by Government departments. According to the SITA Strategic Plan 2020-2025, one of the further objectives of the Agency is to ensure that new applications are written to run on the cloud, as well as that the existing applications are migrated to the cloud.
Satellite Communication
In 2022, The South African National Space Agency (SANSA) in collaboration with the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory (SARAO) launched a beta version of the Digital Earth South Africa data cube platform. The Digital Earth SA system is expected to enable users to leverage the full geographic data analysis capabilities. The data from commercial satellite providers is distributed to government institutions and state-owned entities, whereas private sector users are only allowed to access open satellite datasets. Additionally, SANSA offers private sector data users Analysis Ready Data (ARD) products at an affordable cost.
The SANSA focuses on four programme areas: Earth Observation, Space Engineering, Space Operations, and Space Science. SunSat was the first satellite built in South Africa and launched into orbit in 1999. SumbandilaSat, constructed in collaboration with Stellenbosch University, the CSIR, and SunSpace, was launched by Roscosmos in 2009 on a Soyuz-2 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. In 2012, the SANSA started the development of the country’s third Earth Observation Satellite (EO-Sat1). South Africa’s first cubesat, ZACube-1 (also known as TshepisoSat), was launched in 2013, whereas ZACube-2, which used to be the most advanced nanosatellite in Africa, was launched in 2018 by Roscosmos as well.
Author: Sukhova Daria
Have you spotted a typo?
Highlight it, click Ctrl+Enter and send us a message. Thank you for your help!
To be used only for spelling or punctuation mistakes.